
Medical technology and the importance of innovative IT processes: Where is the growing industry headed?
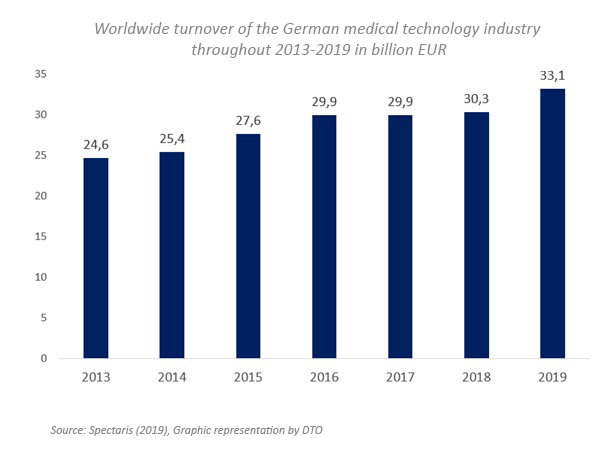
The central driver within the medical industry is technical progress. This has an impact on various areas. In our article, we explain which current developments in the field of medical technology there are in combination with IT developments. Technological progress leads to an evolution within an industry that has always been driven to change. All in all, the medical technology industry is an industry in growth. This has been demonstrated by the development over the past few years. In 2019, the turnover in the MedTech sector was around 33 billion EUR.
The industry is characterized by medium-sized companies both in Germany and internationally. In Germany, the central medical cluster is in Baden-Württemberg. in recent years, medical technology companies in Baden-Württemberg have established a good network of suppliers and customers together with clinics and other medical providers. With more than 600 companies, the southwest of Germany is one of Europe's leading locations in the field of medical technology. Major international companies such as Aesculap AG and Karl Storz GmbH & Co. KG are just as active in the industry as many small and medium-sized companies.
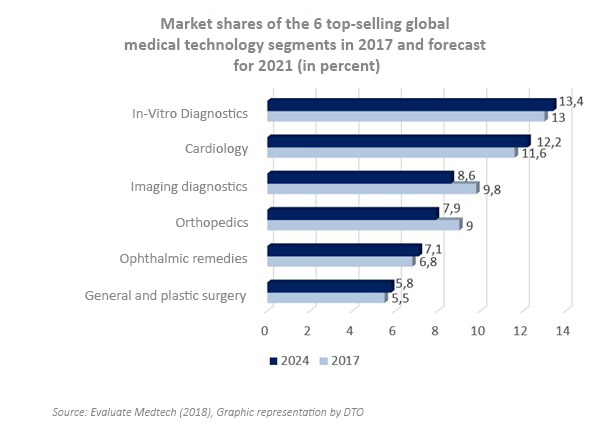
The strongest sales drivers in the medical technology sector are in-vitro diagnostics, cardiology and imaging diagnostics. A certain market saturation can already be observed in these areas. This is partly due to the fact that the innovation segments are primarily located in smart structures. Smart structures are the linking of medicine and technology, creating innovative process optimization. Read on to find out what exactly innovative processes these are.
Technological trends in the medical industry
The greatest influence on medical technology progress is certainly digitalization. In our last article, we already addressed this topic with a concrete case study. Now we are taking a look at other trends from a bird's eye view. Microsystems engineering, nanotechnology and optical technologies are setting the miniaturization of products in motion. The state of the art today is such that we can talk about implantable microsystems that function actively or passively, sensorially, telemetrically or with nerve coupling. The type of surgical interventions will also change fundamentally: In the future, these will be performed even more frequently with minimally invasive surgery (image-guided, catheter-based, and endoscopic).
In addition, molecularization - represented by biotechnology, cell and tissue technology - is establishing itself. Medical technology will become more important for regenerative medicine, especially when research in cell and tissue technology is applied. The next major step in the healthcare revolution, as in many other areas, will be artificial intelligence (AI), intelligent data analysis and data use via algorithms that are constantly learning and improving. As a supportive supplementary tool, systems that enable a more precise hit probability in diagnoses are existentially suitable for minimizing the potential for errors during workload peaks when it comes to physicians.
Problem areas of operative implementation
There is still a lot to do before the apparent change is implemented in operative practice. In addition to prestige projects such as those implemented at the University Medical Center Hamburg, there are overall start-up difficulties: More than half of the hospitals currently do not have their own digital strategy, and implementation is often still lacking. The reasons why there is often a lack of direction in terms of digitalization are very diverse:
- The financing possibilities often cause difficulties.
- Another obstacle is the lack of IT compatibility or interoperability.
- A process standstill due to unsolvable barriers during the IT changeover represents a security risk, which means that this important issue is not addressed.
- Other times the problem lies structurally deeper: If the IT infrastructure is missing in the core processes of a hospital, no IT or digital strategy can be implemented in this inadequate foundation.
Another important issue is data protection. If you open up your processes to a higher degree of digitization, the danger of cyber attacks and security gaps is present in general. This being said, politicians have promised their support in this matter. The law for secure digital communications and applications in the healthcare sector came into force during the end of 2015. This eHealth law is intended to help ensure that the undeniably great opportunities offered by digitization in the German healthcare system are better exploited in the future. Among other things, the law promotes telemedical treatment options and electronic medication plans. The law should be implemented by 2021. But what are treatment facilities able to achieve on their own?
Implementation of IT processes
It is not always possible to implement a holistic digital strategy directly, so it is necessary to selectively choose the processes that can be standardized. Light factors that do not change the entire process chain of a hospital are, for example, the automatic check-in of a patient using an electronic health card, the tracking of patients through the hospital or the automatic transfer of test results to mobile devices. Furthermore, it is advantageous for hospital operators to orientate themselves with already existing reference projects, i.e. to obtain specialist input before implementation. While commercial factors such as required investment funds and running costs are easy to quantify, one of the most important things is to carefully consider the sensitive points a digital strategy can first address. Typical questions to determine where digitization can be effective are, for example, 'How is it possible to optimize the patient stay (without qualitative restrictions for the patient?)', 'Which coordinative processes can be optimized?' Another important point to consider is the measurement of efficiency. 'Was the pilot project successful?' 'Are the changed processes qualitatively measurable?'
More Information
If you would like more information on this topic, please contact us. We are also happy to help you with all other questions within industrial market research and strategic consulting.
Text written by Kai Wichelmann
Sources:
https://www.mckinsey.de/publikationen/digitalisierung-chance-mit-milliardenpotenzial
https://www.bvmed.de/de/technologien/trends/medtech-trends